Scientists create artificial DNA that can be transcribed by a natural enzyme ( phys.org )
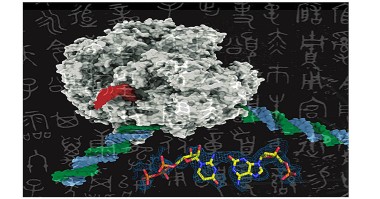
The genetic alphabet contains just four letters, referring to the four nucleotides, the biochemical building blocks that comprise all DNA. Scientists have long wondered whether it's possible to add more letters to this alphabet by creating brand-new nucleotides in the lab, but the utility of this innovation depends on whether or not cells can actually recognize and use artificial nucleotides to make proteins.
Now, researchers at Skaggs School of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences at the University of California San Diego have come one step closer to unlocking the potential of artificial DNA. The researchers found that RNA polymerase, one of the most important enzymes involved in protein synthesis, was able to recognize and transcribe an artificial base pair in exactly the same manner as it does with natural base pairs.